How Doctors Identify and Evaluate a Break
A fracture is more than just a broken bone, it's a structural injury that needs precise evaluation before treatment begins. Accurate diagnosis helps doctors understand the type, severity, and location of the fracture, decide whether surgery is needed, and predict recovery time. Early and correct diagnosis doesn't just shorten healing time, it also reduces complications like malunion, non-union, or infection.
Whether caused by a fall, sports injury, or accident, a fracture requires prompt diagnosis to prevent further complications and ensure proper healing. But not every fracture is visible or obvious. Hairline cracks or stress fractures, for example, may only cause mild pain or swelling at first.
Identifying such hidden injuries early ensures timely immobilisation, proper healing, and fewer long-term problems.
Learn more on Fracture Risks & Complications
Your doctor starts with a physical examination and history-taking to understand how the injury occurred. They check for visible deformity, swelling, tenderness, abnormal movement, and changes in skin colour or sensation. In some cases, doctors also assess blood circulation and nerve function near the injury to rule out associated damage.
Various imaging techniques provide detailed views of the fracture. The choice depends on the suspected fracture type, location, and complexity. Advanced imaging helps create a complete picture for accurate treatment planning.
The most common and first-line diagnostic tool. An X-ray shows the position, alignment, and extent of a fracture. It helps identify clean breaks, displaced bones, or hairline cracks that are invisible to the eye.
Used when soft tissue injury or hidden fractures (like stress fractures) are suspected. MRI provides detailed images of ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and bone marrow, offering a complete picture of internal damage.
CT scans give a 3D view of the fracture site and are especially useful for complex or joint-related fractures such as the pelvis, hip, or spine. They help doctors plan surgical treatment precisely.
For patients with osteoporosis or multiple fractures, a DEXA scan measures bone mineral density. This helps identify whether fragile bones or metabolic issues contributed to the injury and guides preventive care for the future.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Ignoring symptoms can lead to delayed diagnosis and poor healing outcomes.
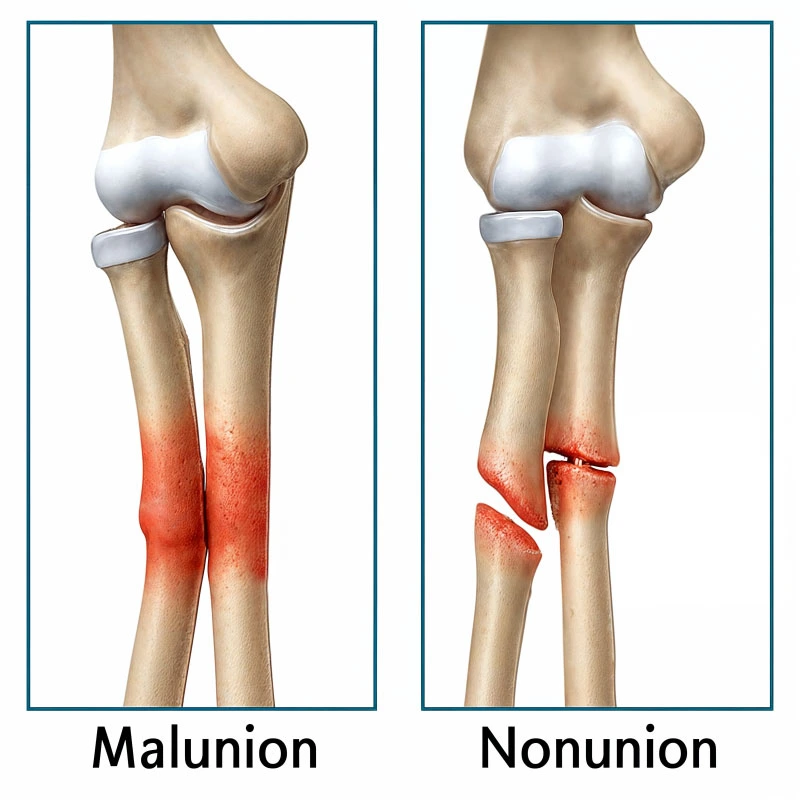
Bones heal in the wrong position, leading to deformity and limited function.
Fracture fails to heal completely, requiring advanced treatment.
Persistent discomfort and limited mobility affecting quality of life.
Bone tissue death due to disrupted blood supply.
No. X-rays confirm the type and extent of a fracture. Without one, it's easy to misjudge the injury and delay proper treatment.
Immediately. Even minor pain or swelling after an injury may hide a small crack that can worsen with movement.
Not always. They are mainly used for complex fractures or when soft tissue damage is suspected.
A stress or micro-fracture might not appear on a standard X-ray. In such cases, MRI or bone scans help confirm the diagnosis.
Regular bone health checks, proper nutrition, and exercises that improve balance and strength help reduce recurrence.